Every 40 seconds, someone in the U.S. suffers a heart attack or stroke. These silent killers strike without warning, but knowing the signs could mean the difference between life and death. Imagine this: You’re at a family gathering when your aunt suddenly clutches her chest, struggling to breathe.
Is it a heart attack? Or maybe your coworker slurs their speech mid-meeting—could it be a stroke? Time is muscle. Time is brain.
In this guide, we’ll decode the critical differences between heart attacks and strokes, arm you with life-saving knowledge, and share science-backed strategies to protect yourself and loved ones.

1. Heart Attack vs. Stroke: What’s the Difference?
Heart Attack
Definition:
A heart attack (medically termed myocardial infarction) occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is severely reduced or completely blocked.
This blockage, often caused by a blood clot forming over a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque in the coronary arteries, deprives the heart of oxygen, leading to tissue damage or death within minutes. There are two primary types:
- STEMI (ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction): A total blockage of a coronary artery.
- NSTEMI (Non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction): A partial blockage.
Key Stats:
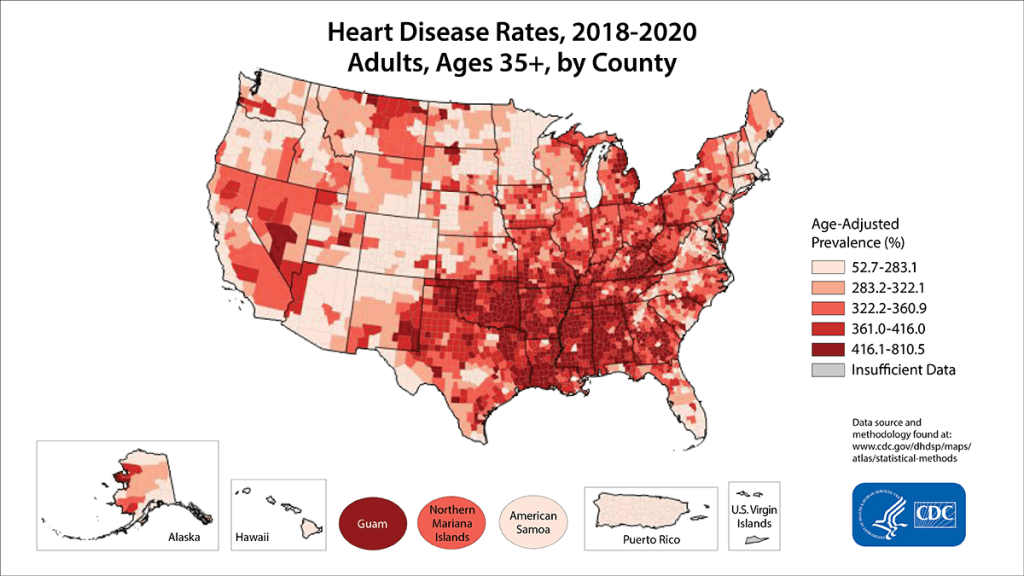
- Leading cause of death in the U.S., claiming 1 in 5 lives annually (CDC, 2023).
- 805,000 Americans experience a heart attack each year—equating to 1 every 40 seconds (American Heart Association, 2023).
- 45% of heart attacks are “silent”, meaning they occur without classic symptoms, delaying critical care.
- Economic Impact: Heart disease costs the U.S. $239 billion yearly in healthcare and lost productivity.
Why This Matters:
Every minute without treatment destroys approximately 10% of the affected heart muscle. Recognizing symptoms early—like chest pain, shortness of breath, or unexplained fatigue—can reduce mortality by up to 50%.
Stroke
Definition:
A stroke, often called a “brain attack”, occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is disrupted, either by a blockage (ischemic stroke, 87% of cases) or bleeding (hemorrhagic stroke). There are two primary types:
- Ischemic Stroke: Caused by a clot obstructing a blood vessel in the brain. Subtypes include:
- Thrombotic (clot forms in a narrowed artery).
- Embolic (clot travels from elsewhere, like the heart).
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Results from a ruptured blood vessel, often due to uncontrolled hypertension or aneurysms.
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): A “mini-stroke” with temporary symptoms, serving as a critical warning sign.
Key Stats:
- 795,000 strokes occur annually in the U.S., with one happening every 40 seconds (American Stroke Association, 2023).
- #5 Cause of Death in the U.S., responsible for 1 in 20 fatalities (CDC, 2023).
- Long-Term Disability: 50% of survivors face mobility issues, and 30% struggle with speech (National Institute of Neurological Disorders).
- Economic Burden: Stroke costs the U.S. $53 billion yearly in healthcare and lost productivity.
Why It Matters:
- Time = Brain Cells: Every minute untreated, a stroke patient loses 1.9 million neurons. Treatment within 3–4.5 hours (using clot-busting drugs like tPA) can drastically improve outcomes.
- FAST Saves Lives: The FAST acronym (Face, Arms, Speech, Time) helps bystanders act quickly—80% of strokes are preventable with early intervention.
2. The Silent Signals: Warning Signs You Can’t Ignore
Heart Attack Symptoms
Classic Symptoms (Men and Women):
- Chest Pain or Pressure
- Often described as a crushing sensation, like “an elephant sitting on your chest”.
- May last longer than a few minutes or come and go.
- Key Stat: 70% of heart attack patients report chest discomfort (Journal of the American College of Cardiology).
- Radiating Pain
- Spreads to the left arm, jaw, neck, or upper back.
- Why It Happens: Nerves in the heart and these areas share pathways, causing “referred pain.”
- Shortness of Breath
- Occurs even without exertion—“like trying to breathe through a straw”.
- Often accompanied by cold sweats, nausea, or lightheadedness.
Heart Attack Symptoms in Women
Women are 50% more likely to experience atypical symptoms, which are often overlooked:
- Extreme Fatigue: Sudden exhaustion, even after rest (reported by 70% of women pre-attack).
- Indigestion or Heartburn: Mistaken for gastrointestinal issues.
- Dizziness or Fainting: Linked to reduced blood flow to the brain.
- Upper Back Pain: Sharp, unexplained pain between the shoulder blades.
Real-Life Example:
Sarah, 48, felt “flu-like fatigue” for days before her heart attack. She dismissed it as stress—a common mistake.
Silent Heart Attacks: The Hidden Danger
- 20-30% of heart attacks are “silent” (no chest pain), especially in diabetics and older adults.
- Red Flags: Prolonged fatigue, mild discomfort, or sudden shortness of breath during routine activities.
What to Do Immediately:
- Call 911 if symptoms last >5 minutes.
- Chew Aspirin (325 mg) unless allergic—it can reduce clot size.
Stroke Symptoms
The FAST Acronym: Act in Seconds, Save a Life
- Face Drooping
- One side of the face goes slack or feels numb.
- Test: Ask the person to smile—is it uneven?
- Arm Weakness
- Sudden numbness or weakness in one arm (often the left).
- Test: Can they raise both arms equally?
- Speech Difficulty
- Slurred speech, gibberish, or inability to form words.
- Test: Ask them to repeat a simple sentence (e.g., “The sky is blue”).
- Time to Call 911
- Every minute = 1.9 million brain cells lost.
- Note symptom onset time—clot-busting drugs (tPA) must be given within 4.5 hours.
Lesser-Known but Critical Signs
- Sudden Confusion: Incoherent thoughts or inability to understand others.
- Vision Loss: Blurred or blackened vision in one/both eyes.
- Severe Headache: “Worst headache of my life” (common in hemorrhagic strokes).
- Balance Issues: Stumbling, dizziness, or loss of coordination.
Silent Strokes: The Invisible Threat
- 1 in 3 adults over 70 has had a silent stroke (MRI findings).
- Red Flags: Mild memory lapses, slight balance problems, or mood changes.
Why FAST Works
- Proven Impact: FAST-trained bystanders increase ER arrival speed by 40% (Stroke Journal, 2022).
- Global Use: Adopted by WHO in 100+ countries.
Immediate Action Plan:
- Call 911 (even if symptoms fade—TIAs warn of future strokes).
- Do NOT give aspirin (could worsen hemorrhagic strokes).
- Stay Calm: Note symptom onset time for medical teams.
3.Why Every Second Counts: The Life-Saving Power of Early Action

Heart Attacks: The Race Against Time
- Heart muscle dies rapidly: During a heart attack, 1 billion heart cells are lost every 30 minutes without treatment (Journal of Cardiovascular Medicine).
- Golden Hour: Patients treated within 90 minutes of symptom onset:
- Have 50% higher survival rates
- Preserve 80% more heart function long-term
- Critical Tests:
- EKG within 10 minutes of hospital arrival
- Angioplasty (stent placement) within 90 minutes
Strokes: Saving Brain Cells Minute-by-Minute
- tPA Window: The clot-busting drug alteplase works best when given:
- Within 3 hours for most patients (up to 4.5 hours in select cases)
- Can reduce disability by 30% (American Stroke Association)
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: For large clots, this surgical procedure can be effective up to 24 hours post-stroke in eligible patients
- 70% of cardiac arrests happen at home
- Immediate CPR can double or triple survival chances
Real Impact Story:
James, 47, survived a massive heart attack because his wife recognized symptoms and called 911 immediately. Doctors restored blood flow in just 68 minutes – he returned to work 6 weeks later with minimal heart damage.
Action Steps Everyone Should Know:
- For Heart Attacks:
- Call 911 immediately (don’t drive yourself)
- Chew 325mg aspirin unless allergic
- For Strokes:
- Use the FAST test
- Note exact symptom onset time
- For Cardiac Arrest:
- Begin hands-only CPR at 100-120 compressions/minute
- Use an AED if available
Visual Guide Suggestion:
Include a timeline graphic showing:
- Heart attack: Tissue loss vs. treatment time
- Stroke: Brain cells saved with tPA at 1hr vs. 3hrs
Key Statistics:
- Patients who recognize symptoms early are 3x more likely to survive without major complications
- Every 15-minute delay in treatment reduces life expectancy by 1 year on average
4. Prevention: Your Shield Against Cardiovascular Disasters
Science-Backed Strategies to Outsmart Heart Attacks and Strokes
1. Diet: Your Plate as Medicine
Mediterranean Diet – “The best diet for heart health”
- 30% Lower Risk: Linked to a 30% reduction in heart disease (Harvard Health).
- Key Components:
- Olive Oil: Rich in monounsaturated fats (reduces LDL cholesterol).
- Fatty Fish: Omega-3s lower inflammation (aim for 2 servings/week).
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds improve arterial health.
- Colorful Produce: Antioxidants in berries and leafy greens combat oxidative stress.
DASH Diet: Proven to lower blood pressure by 11 mmHg in 2 weeks (NIH).
Avoid:
- Added Sugars: Linked to 3x higher stroke risk in women (Journal of the American Heart Association).
- Ultra-Processed Foods: Increase heart attack risk by 12% per 10% intake (BMJ).
2. Exercise: Move to Protect Your Heart
150 Minutes/Week Rule – “Exercise to prevent heart attacks”
- Moderate Activity: Brisk walking, cycling, or swimming lowers LDL cholesterol by 10%.
- HIIT Workouts: Just 20 minutes, 3x/week improves endothelial function (American College of Cardiology).
- Strength Training: Reduces visceral fat (a key driver of hypertension).
Pro Tip: Use a fitness tracker to hit 7,000+ daily steps—linked to a 50% lower mortality risk (JAMA Network Open).
3. Monitor: Know Your Numbers
Blood Pressure
- Target: <120/80 mmHg.
- At-Home Checks: 2x/day if hypertensive.
Cholesterol
- Ideal LDL: <100 mg/dL (diabetics: <70 mg/dL).
Blood Sugar
- Fasting Glucose: <99 mg/dL.
- HbA1c: <5.7% (prediabetes: 5.7–6.4%).
Tech Tools:
- Smartwatches: Track heart rate variability (HRV) for stress management.
- Home BP Monitors: FDA-approved devices like Omron Series.
4. Stress Management: The Silent Game-Changer
- Chronic Stress: Doubles stroke risk (Neurology Journal).
- Proven Tactics:
- Mindfulness Meditation: Lowers cortisol by 20% in 8 weeks.
- Yoga: Reduces arterial stiffness in 12 weeks (European Journal of Preventive Cardiology).
5. Sleep: The Underrated Protector
- <6 Hours/Night: 27% higher atherosclerosis risk (Journal of the American College of Cardiology).
- Sleep Apnea: Untreated cases triple heart attack risk. Fix with CPAP therapy.
5. Stories of Survival: Hope Beyond the Crisis
Maria’s Story: The FAST Response That Saved a Life
“I Thought It Was Just Dizziness…”
At 68, Maria was gardening when suddenly:
- Her left arm went numb
- Words slurred mid-sentence
- The world spun violently
Critical Actions That Made the Difference:
- Her granddaughter recognized the FAST signs immediately
- EMS arrived within 8 minutes (national average: 14 minutes)
- Received tPA at the hospital within 45 minutes of symptom onset
Today:
- Leads stroke awareness workshops at local churches
- Featured in the American Stroke Association’s “Survivor Stories” series
- Key Message: “Don’t second-guess – call 911 the moment something feels ‘off’!”
David’s Journey: From Heart Disease to Marathon Finisher
Diagnosed at 45 with:
- 90% blockage in LAD artery (“widowmaker”)
- LDL cholesterol of 190 mg/dL
- BMI of 32
His 12-Month Transformation:
- Diet Revolution:
- Switched to plant-based Mediterranean diet
- Eliminated processed sugars completely
- Exercise Protocol:
- Started with 10-minute walks, progressed to running
- Completed Chicago Marathon 18 months post-diagnosis
- Medical Partnership:
- Works closely with a preventive cardiologist
- Takes low-dose statin as safety net
Results:
- Reversed atherosclerosis per latest angiogram
- Resting heart rate improved from 82 to 48 BPM
- Featured in Men’s Health “Heart Comebacks” issue
“Like Maria and David, your experience could inspire others. Share your journey in the comments – you might just save someone’s life.”
FAQ: Heart Attacks vs. Strokes – Life-Saving Knowledge
• What’s the key difference between a heart attack and a stroke?
A: A heart attack blocks blood flow to the heart (1 every 40 seconds in the U.S.), while a stroke disrupts brain blood flow (795,000 cases/year). Heart attacks damage heart muscle; strokes kill brain cells (1.9 million neurons lost/minute untreated). Both require immediate 911 calls.
• Do women experience different heart attack symptoms?
A: Yes! 70% of women report atypical symptoms like extreme fatigue, indigestion, or upper back pain (vs. chest pain in men). Silent heart attacks are 50% more common in women. The CDC urges awareness—45% of heart attacks are missed due to subtle signs.
• What does the FAST acronym mean for strokes?
A: FAST saves lives:
Face drooping
Arm weakness
Speech difficulty
Time to call 911
Acting FAST cuts disability risk by 30%. TIAs (“mini-strokes”) require urgent care—20% lead to major strokes within 90 days.
• Why is aspirin advised for heart attacks but not strokes?
A: Aspirin thins blood, helping heart attack clots. But in hemorrhagic strokes (13% of cases), it can worsen bleeding. Never guess: Call 911 first. tPA clot-busters work only for ischemic strokes and must be given within 4.5 hours.
• How can I prevent 80% of cardiovascular events?
A: Science-backed strategies:
1. Mediterranean diet: 30% lower heart disease risk (Harvard).
2. 150 mins/week exercise: HIIT improves artery health.
3. Monitor BP: <120/80 mmHg goal.
4. Sleep 7-8 hrs/night: Reduces atherosclerosis risk by 27%.
5. Stress management: Yoga cuts stroke risk by 20%.
Conclusion
Every minute wasted during a heart attack means 10% more heart muscle destroyed, and every untreated second of a stroke claims 1.9 million brain cells.
These aren't just statistics—they represent lives that could be saved with immediate action. Recognizing symptoms and seeking emergency care isn't optional—it's survival.
Your next decision—whether calling 911, chewing aspirin, or performing the FAST test—can literally rewrite someone's fate.
The difference between tragedy and recovery lies in what you do this very moment.
This knowledge doesn't just empower you—it makes you someone's lifeline. Will you be ready when seconds count?
Discover more from WST
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.




